Utilize Github Actions for Angular App Deployment on Firebase Hosting
Use Github Actions to Deploy Angular Apps on Firebase Hosting
This is another post about how to achieve this goal. Since I need to cover it for the series on using ComponentStore, I will write a brief(was more long than I thought) post explaining the process.
Part 1: Add and configure Firebase with our project
The first step is to install firebase-tools. This lets us use Firebase directly through our console and helps us set up everything to work with Firebase.:
npm install -g firebase-tools
Log in to Firebase through the console:
firebase login
Follow the steps until prompted to open a screen to log in to Firebase using your Gmail account. At the end of the process, you should see an image similar to this in your browser:
After finishing these steps, we can now use firebase-tools to make a project on Firebase Hosting and set up everything automatically:
firebase init hosting
This will guide us through 3 steps, which include:
- Initialize the project:
Create all the files necessary in our repo, create the project in Firebase, and set up the project and credentials in our Google Cloud.
Choose Hosting:
Configure files for Firebase Hosting and (optionally) set up GitHub Action deploysSelect
Create a new projectSet a
unique project idtry to type a unique ID, if not type something unique, fail all, and start over again.Set a
name for your project(same here)

- Setup del hosting:
What do you want to use as your public directory?dist/series-workspace (if you are not sure, this can be changed later infirebase.jsonfile)Configure as a single-page app (rewrite all urls to /index.html)?Yes, Angular is a single-page app (SPA)Set up automatic builds and deploys with GitHub?Yes, this is very important, herefirebase-toolswill try to connect to Github and get info on the current git, will open a login page of an app (firebase app) trying to use GitHub to retrieve data from our account. Here is everything is ok, you will see in the console✔ Success! Logged into GitHub as YOUR_GITHUB_USER_HEREFor which GitHub repository would you like to set up a GitHub workflow?here, I only want a confirmation of the name of the repo(OUR_GITHUB_USER/REPO_NAME)if it is wrong type the correct
- Create the Actions files:
Set up the workflow to run a build script before every deploy?Yes, this is important, to this question, we confirm we wantfirebase-toolsto create automatically a Github Action file for our repo used when you do a Pull Request in Github.What script should be run before every deploy?yarn install && nx build series-workspace, in my case, if not sure, can change it later in the YAML file.Set up automatic deployment to your site's live channel when a PR is merged?Yes, this is for creating another Github Action to detect a merge to main.What is the name of the GitHub branch associated with your site's live channel?main, in my case.
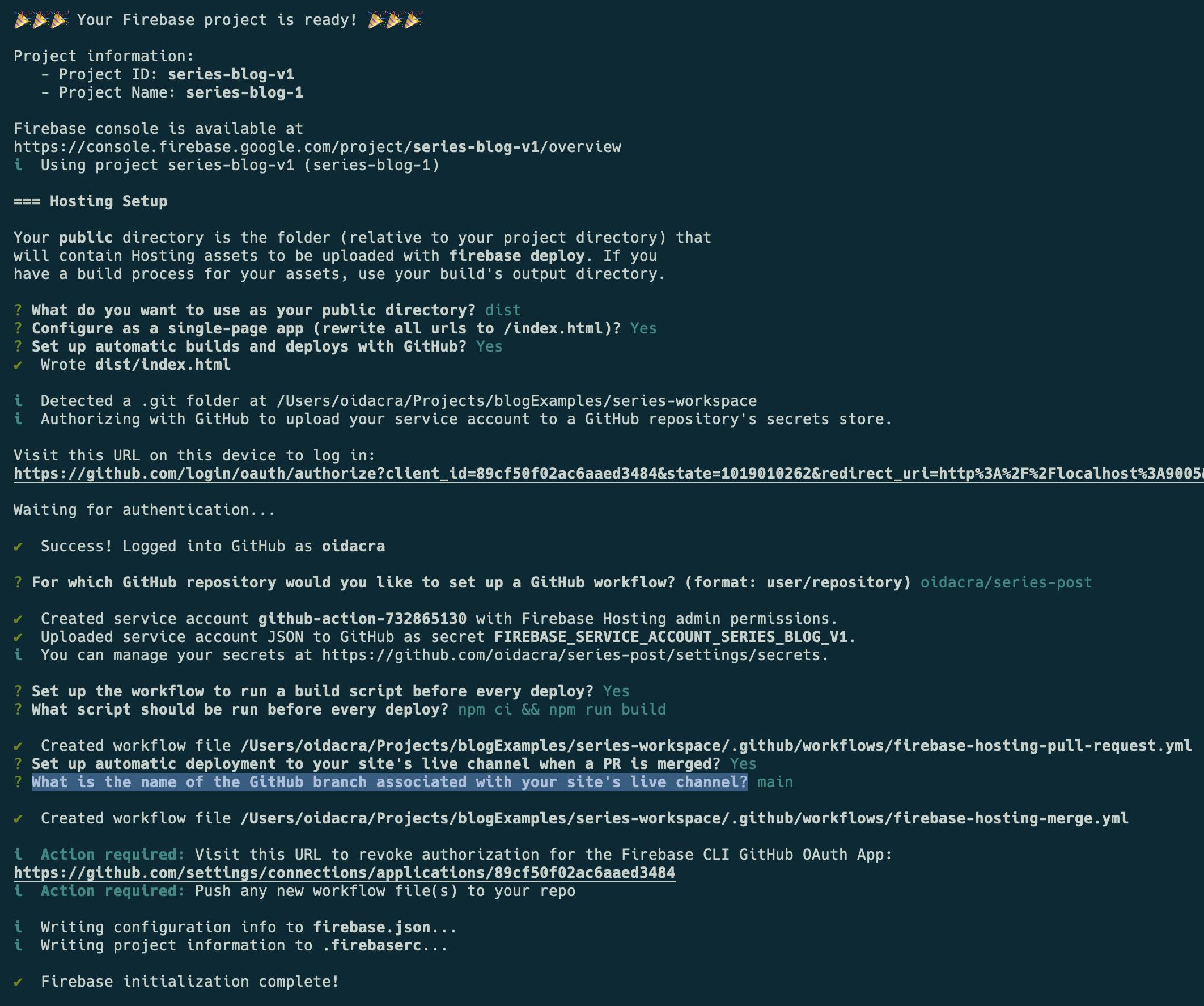
Now we have 4 new files in our repo:
firebase.jsonIs the configuration file for Firebase in our project, in this case, we only will see the configuration ofhosting, there we can change the correct path to thepublicfolder, the other values are left as is..firebasercHere, you can see the project id..github/workflows/firebase-hosting-pull-request.ymlGitHub Actions trigger when detecting a new PR.github/workflows/firebase-hosting-merge.ymlGithub Action trigger when you do a merge tomain
In the firebase-hosting-pull-request.yml, you'll notice two secret tokens. FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SERIES_PROJECT_V1 is created automatically in our repository secrets configurations (it contains a credential created automatically in our Google Cloud). The other token, GITHUB_TOKEN, is set automatically by GitHub itself when running the GHA.

This is our firebase-hosting-pull-request.yml base action file:
# This file was auto-generated by the Firebase CLI
# https://github.com/firebase/firebase-tools
name: Deploy to Firebase Hosting on PR
'on': pull_request
jobs:
build_and_preview:
if: '${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name == github.repository }}'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- run: yarn install && npx nx build series-workspace
- uses: FirebaseExtended/action-hosting-deploy@v0
with:
repoToken: '${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}'
firebaseServiceAccount: '${{ secrets.FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SERIES_V1_DB }}'
projectId: series-v1-db
Part 2: Let's improve the GitHub Action
Github Actions enable us to perform checks, compile code, create Docker images, and do everything necessary to deliver our applications. There are many ways to accomplish the same tasks, but it depends on the size and complexity of our app. With that in mind, let's define our requirements for the time being:
When creating a
PR, we need to:Ensure that the
testsrun without failuresEnsure that the
lintruns without failuresEnsure that our code can
buildwithout failuresPush to Firebase Hosting to
previewchannel to take a look at the functionality.
When performing a
merge:Ensure that our code can
buildwithout failures, and additionallyPush to Firebase Hosting to
livechannel
That's our plan; for simplicity, we will continue using the generated Github action for PR (firebase-hosting-pull-request.yml) and merge (firebase-hosting-merge.yml) to main.
With all the requirements for the PR added to the file, this is the final firebase-hosting-pull-request.yml file
name: Deploy to Firebase Hosting
on: # when does the workflow run?
pull_request:
types: [opened, synchronize, reopened, ready_for_review]
branches: [main]
permissions:
actions: read # Needed for nx-set-shas
contents: read # Needed for nx-set-shas
checks: write # Needed for GITHUB_TOKEN
jobs:
build_and_preview: # name of the job
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4 # Checkout the repository at the latest commit
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Fetch all history for all branches so that nx affected can compare against all commits
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3 # Cache node_modules to speed up builds
with:
node-version: 18 # Use the version 18 of Node.js
cache: 'yarn' # Cache node_modules to speed up builds
- name: Install Dependencies
run: yarn install --frozen-lockfile # Install dependencies using yarn with a frozen lockfile
- name: Setup Nx SHA
uses: nrwl/nx-set-shas@v3 # Sets environment variables for commit SHAs, optimizing Nx's change detection for efficient CI processes
- name: Check Git Branch
run: git branch --track main origin/main # This line is needed for nx affected to work when CI is running on a PR
- name: Run Nx Format Check
run: npx nx format:check # Run the format check
- name: Run Nx Affected Commands
run: npx nx affected -t lint,test,build --parallel=3 # Run the lint, test, and build targets in parallel
- name: Deploy to Firebase Hosting Preview Channel
uses: FirebaseExtended/action-hosting-deploy@v0
with:
repoToken: '${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}'
firebaseServiceAccount: '${{ secrets.FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SERIES_V1_DB }}'
projectId: series-v1-db
#channelId: preview by default if you don't specify it.
We can observe a total of 8 steps in our action file, with the first 6 preparing everything to execute the Run Nx Affected Commands npx nx affected -t lint,test,build --parallel=3. This command runs Nx affected for the tasks (-t) lint, test, and build, and includes a flag allowing up to 3 tasks to run simultaneously. With this, we can ensure that everything in our repository is 100% correct before running the last step of our job Deploy to Firebase Hosting Preview Channel.
When the action successfully runs on GitHub, we see something quite similar to this in our PR, under the Checks tab. We can view the list of detected actions, and by clicking on the name of the action (Deploy to Firebase Hosting in our case), we can examine the details of the jobs and all the steps within each job.

Alright, but what about merging to the main branch? For that, we configure the other GHA file, firebase-hosting-merge.yml. This file is similar, with only a few details changed.
name: Deploy to Firebase Hosting on merge
on: # when does the workflow run?
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
build_and_deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4 # Checkout the repository at the latest commit
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Fetch all history for all branches so that nx affected can compare against all commits
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3 # Cache node_modules to speed up builds
with:
node-version: 18 # Use the version 18 of Node.js
cache: 'yarn' # Cache node_modules to speed up builds
- name: Install Dependencies
run: yarn install --frozen-lockfile # Install dependencies using yarn with a frozen lockfile
- name: Run Build App
run: npx nx build series-workspace #build the app
- name: Deploy to Firebase Hosting Preview Channel
uses: FirebaseExtended/action-hosting-deploy@v0
with:
repoToken: '${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}'
firebaseServiceAccount: '${{ secrets.FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SERIES_V1_DB }}'
channelId: live # Deploy to live channel
projectId: series-v1-db
The three (3) main differences are:
- What triggers the action, in this case, a merge (push) to
main.
on: # when does the workflow run?
push: # only trigger with a push to main (PR merged to main)
branches:
- main
- And, what channel we will push the final build, in this case to
livechannel inFirebase.
firebaseServiceAccount: '${{ secrets.FIREBASE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_SERIES_V1_DB }}'
channelId: live # Deploy to live channel
projectId: series-v1-db
- We only do a build, instead of checking lint, test, and format. In the PR, we did all these steps to be sure everything was ok. Now we only need to build the app and ship the code.
- name: Run Build App
run: npx nx build series-workspace #build the app
If you go to your Firebase Console, to the created project, you can see:
Your Current release is replaced with every merge to
main.Previous releases (if you want to do a rollback), and,
Preview channels (Every PR has a different link, and that link will be available for only 7 days)

This approach makes deploying your SPA straightforward, and if you use other Firebase tools like Authentication, Messaging, Functions, Realtime Database, or Firestore, you'll have everything you need to complete your side project without any issues.
Here is the final GHA running in GitHub PR Action and the Merge Action.
Conclusion
GitHub Actions and Firebase Hosting together provide a powerful and efficient way to deploy your Angular applications. By automating the process of running tests, lint checks, and builds before deployment, you can ensure the integrity and reliability of your code. Additionally, the Firebase Hosting's preview and live channels allow for thorough review and testing of your application before it goes live. This process not only simplifies the deployment of single-page applications but also seamlessly integrates with other Firebase tools, making it an ideal solution for completing side projects or even larger-scale applications.
Leave a comment and let me know if something is missing or if you want more details about any step.


